Epigenetics
The Science of change
Dr Nitika Sobti
Founder – Virtue Baby
Sr. Consultant (Obstetrics and Gynaecology)
Max Super Speciality Hospital
Shalimar Bagh

The word epigenetics means things imposed "on top of genetics".
The study of modifications to DNA that promote changes in gene expression without altering the DNA sequence
Nurture
Nurture
Epigentics
History of Epigenetics
Conrad Waddington coined the term, “epigenetic. Waddington’s concept was a pivotal concept in developmental biology as it attempted to explain how a static set of DNA sequences could dynamically give rise to a complex organism. Pioneering work by Waddington also demonstrated compelling evidence for inheritance of a seemingly acquired characteristic in drosophila fruit flies.

Studies
- Johns Hopkins University- First Center for Comprehensive Study of Epigenetics
- Harvard University -Epigenetic control of gene expression, epigenetics in mammalian development, and epigenetics in cancer are few topics from Harvard's researchers
- The National Cancer Institute of the US - Research areas include DNA methylation, heterochromatin cancer pathogenesis, the role of DNA methylation in health and disease, and tumor phenotypes.
- University of Virginia - topics are the histone code, chromatin structure, and histone-chromatin crosstalk.
- The University of Cambridge - epigentics in cancer and other diseases, such as diabetes, Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, and Huntington's disease, and the role of epigenetics in cells, particularly in mammalian development.
In an article published in Time Magazine in 2010 entitled
“Why Your DNA Isn’t Your Destiny,” the work of Dr. Lars Olov Bygren, a preventative-specialist and researcher, is discussed. He discovered that the dietary and lifestyle conditions affected the genetic expression of not only the individual, but also their children and grandchildren. He concludes “it is through epigenetic[s]…that environmental factors like diet, stress and prenatal nutrition Prenatal nutrition, Prenatal Stress, Postnatal Behavior can make an imprint on genes that are passed from one generation to the next.”
GENETICS IS THE HARDWARE & EPIGENETICS IS THE SOFTWARE.

Methylation
DNA methylation is an epigenetic mechanism used by cells to control gene expression. A number of mechanisms exist to control gene expression in eukaryotes, but DNA methylation is a commonly used epigenetic signaling tool that can fix genes in the “off ” position.
DNA methylation and disease
Researchers are currently looking at the links between DNA methylation and human diseases such as lupus, cancer, muscular dystrophy and various congenital defects. Their findings could be significant in aiding the development of therapies and for understanding and preventing conditions that develop during embryonic development as a result of abnormal methylation of the X chromosome and gene imprinting.
- The human genome contains 25000-35000 genes as well as switches controlling them. A genome is a complete set of DNA in a cell. DNA carries the instruction for building all the proteins that make each living creative unique.
- These 25000-35000 genes make only 5% of genome the rest consisting of switches (epigenome). As we might say we have a 100 page book & 95 pages are instructions how to read, the book.
From where does this epigenetic information get laid on our chromatin
- Much of it happens during our embryonic development.
- When you were first conceived you were just a group of few a undifferentiated embryonic stem cells, your chromatin did not have epigenetic marks/switches on it. It is only when our cells begin to divide & receive signals & information from surrounding cells that epigenetic marks begin to accumulate & genes began to turn on and off. Each cell type expresses only these genes required for its specific function. This modification is determined by the interplay between enzymes which are controlled by epigenetic signal pathways-that respond to changes in the cell’s local environment.
Perturbations of these signaling pathways can predisposed to the development of diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer, Schizophrenia says Peter Becker (2015) of Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich.
Epigenetic marks can be influenced by the environment

Environmental Genetics
- The early emotional environment can lead to long lasting epigenetic changes. One example is the epigenetic changes shown in a special type of mouse AGOUTI MOUSE.
- Both mice and people have a gene called agouti (Dolinoy, Huang, & Jirtle, 2007). When a mouse’s agouti gene is completely unmethylated mouse has a yellow coat color, is obese, and prone to diabetes and cancer. When the agouti gene is methylated (as it is in normal mice) the coat color is brown and the mouse has a low disease risk. Fat yellow mice and skinny brown ones are genetically identical. The fat yellow mice look different because they have an epigenetic
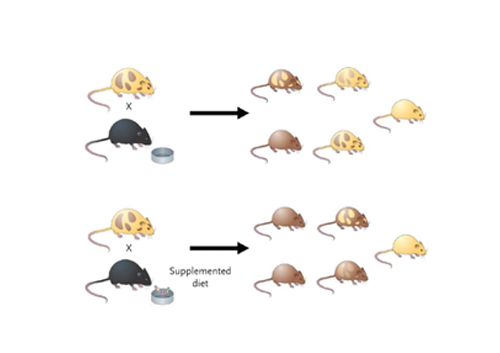
- When pregnant yellow agouti mice were not fed methyl-rich foods, no folic acid –caused decreased methylation of agouti gene, thus giving birth to obese yellow mice.
- When pregnant yellow agouti mice were fed methyl-rich foods (even if they were exposed to chemicals BPA) their offsprings were brown mice.
- So these genetically identical mice look, so radically different due to epigenetic changes caused in the womb by pregnant mother ’s diet.
- Our findings provide a framework, charged messages regarding fear and anxiety also pass modified brain chemistry to their offspring” (Dias et al, 2015).
There is compelling evidence that epigenetic dysregulation underlines the observed associations between adult disease and adverse environmental and nutritional conditions early in development as suggested in
"Hunger Winter Studies" – Baugh principal researchers, Duke University neurobiologist, stated that starvation early in life can alter an organism for generations.
Social Epigenetics
- Researchers at the University of Zurich “traumatized” male mice by separating them from the mother at unpredictable times in the first two weeks of life.
- The study led by Professor Isabelle Mansuy in 2014 - traumatic experiences affect metabolism in the long-term and that these changes are hereditary ( much alterations in the levels of micro RNA in sperm).
Transgenerational Inheritance of Behavioral Traits
- Affectionate maternal care given to female rats pups post natally results in them giving some quality care to their offspring when they become mothers. Abusive and neglectful caregivers are known to leave children particularly susceptible to cognitive and emotional dysfunction. Indeed, there is a significant association of reported childhood maltreatment and the later diagnosis of adolescent and adulthood schizophrenia, borderline personality disorder, posttraumatic stress disorder, and major depression.
- Higher levels of care-taking behavior during the first week of life modifies gene transcription throughout the lifespan and promotes adult behavior that is characterized by stress resilience and increased maternal care.
- Researchers at the University of British Columbia have demonstrated that human infants of mothers with high levels of depression and anxiety during the third trimester have increased methylation of the Nr3c1 gene promoter in cord blood cells (Devlin, Brain, Austin, & Oberlander, 2010).
- Patrick McGowan found that in suicide victims the levels of this gene were very low. This gene produces a protein GR-Low level of this GR receptor is also found in mood disorders, schizophrenia, and suicide.
- Delivery by elective cesarean section also has shown an increased risk of certain diseases, such as Asthma, Type 1-diabetes, Obesity, Celiac Disease, and Cancer.
- It is evident from our survey of recent discoveries in epigenetics how nature (genes) and nurture (the environment) work in concert.
- The only thing we know for sure is that we are a product of dynamic interaction between nature and nurture that nothing about us is written in stone and, therefore, as long as we breathe, we are a work in progress, constantly changing. Epigenetic modifications are dynamic and potentially reversible processes.
Three simple steps
- Eat plenty of cruciferous vegetable such as broccoli and cauliflower. They contain antioxidant that enhance our tumor fighting genes and what way lower our risk of developing cancer.
- Exercise regularly. Exercise has been shown to prevent stem cells fro turning into fat cells.
- Do not suffer silently of stress, anxiety and depression. They affect negatively the epigenome. These conditions need to be dealt with as soon as they arise.
Key Take Away
- An individual’s adult health is heavily influenced by early prenatal physiological factors affecting the mother such as food, pollution, and radiation.
- The unborn child will adjust as best it can to the external environment he/she is going to encounter upon birth by way of epigenetics changes.
- At least parts of the changed genetics code can be passed on to future generations.
- Genes don’t make you who you are. Gene expression does. And gene expression varies depending on the life you live.
- Gene activity cranks up or spins down in response to changes in your environment.
- Our social lives, our interactions with others and ourselves can change our gene expression with a rapidity, breadth, and depth previously unknown.
