FETAL PSYCHOLOGY
Dr Nitika Sobti
Founder – Virtue Baby
Sr. Consultant ( Obstetrics and Gynaecology)
Max Super Speciality Hospital Shalimar Bagh
Of all our existence, the 9 months we live ,the womb is the most eventful for our growth and development.
"The history of man for the nine months preceeding his birth would be far more interesting and contain greater moments of excitement than all the years that follow it"
Peter Harper: Director Fetal Behaviour Research Centre, Queens University, Belfast
CLASSICAL VIEW: develop from a blueprint from the parents genes--- healthy baby
Not any more !! Dr Pathik Wadhwa ( univ. of Kentucky college of Med ) At each stage : organism uses cues from the environment to decide how best to construct itself within the given parameters of the genes
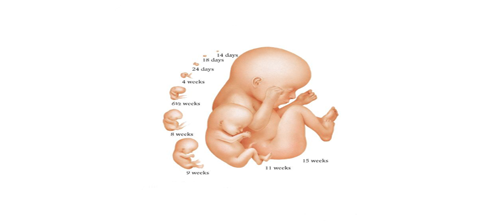
Duration of Prenatal Periods
-
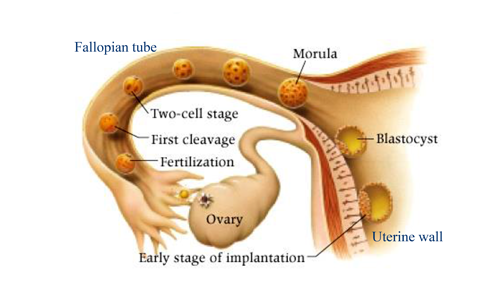
Germinal period (single-cell zygote morula blastocyst) - Conception to attachment (8-10 days later)
-
Embryonic period (embryo) - Attachment to end of 8th week (when all major organs have taken primitive shape)
Basic organ system formation
-
Fetal period (fetus) - 9th week (with first hardening of the bones) until birth
Growth and maturation
Germinal Period
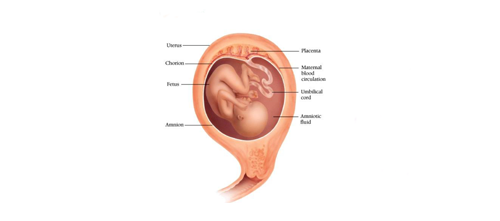
Fetal Period
Begins with skeletal ossification, From week 8/9 until birth, From 1¼ - 20 inches, From 8 - 3250 grams
Embryonic Period
-
Begins with implantation and lasts for about 6 weeks
- - Basic organs formed; sexual differentiation occurs
- - Organism begins to respond to direct stimulation (e.g., will turn its head in response to a light touch around the mouth)
-
Developmental patterns
- – Cephalocaudal: Proceeds from head down
- – Proximodistal: From middle of organism out to the periphery
Fetal Development
-
10th week: Intestines in place; breathing and jaw-opening movements
-
12th week: Sexual characteristics; well-defined neck; sucking and swallowing movements
-
16th week: Head erect and lower limbs well-developed
-
5th month: As many nerve cells as it will ever have
-
7th month: Eyes open and lungs capable of breathing
-
8th month: Many folds of the brain present
-
9th month: Brain more convoluted
-
Fetus doubles in weight in final weeks before birth
Germinal Period: Key Concepts
"It is all in the genes" or Epigenetics ????
Interactions between the cells and their environment generate the new cell forms and emergence of body organs
Patterns established in the womb Influenced by maternal diet / psychological state/ environment of the womb

Myths About Fetus
BABIES DO NOT FEEL - even if they feel they will not remember later.
Babies do not think, are without consciousness- Very limited brains – brain is unable of superior functions as thinking, meaning atribution or memory. Myelination only completed during adolescen, it only works when it’s completed?
Age myth – we see all age groups diferent from our own, as inferiors in all levels: embryo, fetus, newborn, child, teenager or elderly
Chamberlain, the mind of your newborn baby, 1998
Myths About Fetus
- A 3mm neural tube will grow into a whole brain containining 100 billion neurons and 100 trillion connections.
- Proliferation( production of new neurons) starts at 5wks continues upto 18mths of age.
- Precursor cells give rise to neurons which migrate to specific brain areas which perform specific functions.
- The developing brain sheds innumerable excess neurons, dendrites and synaptic connections ( pruning), which is under environmental control.
Parts and functions of fetal brain
-
Brainstem – fashioned around 33rd day of gestation ,matures completes myelination by 7th gestational month.
-
Medulla- controls gross body movement, HR, respiration and head turning. Spon movement by 7thwk, first breath by 10thwk
-
Pons- controls the vibratory acoustic perception, head turning and FHR acceleration
-
-
Forebrain – develops at term and over the following weeks and months
- - Generates high order cognitive activity and purposeful behaviour which is responsible for expression and experience of true emotions
FETAL BEHAVIOUR AND COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT
- Fetus is capable of considerable behavioural complexity
- Complex actions are mediated by brainstem with minimal forebrain participation as similar behaviours are demonstrted by anencephalics
- Actions like head turning, eye movements , crying, screaming smiling are complex behaviours which are also mediated through brainstem
- Thus brainstem also appears capable of learning related activity and cognitive ability
"When a mother is extremely stressed during pregnancy , she produces hormones called glucorticoids that cross the placenta to the baby and can alter the development of kidney and heart"
Dr Karen Moritz: Univ. of Queensland
Fetal Investigation
-
Historically, fetal research was merely about physical evolution, because the mechanisms of prenatal consciousness - and the means to measure them – were not thought to exist.
-
William James in 1981 first described developmental fetal psychology increase in our knowledge of the sensory ability of the fetus and its consciousness and how the internal and external factors combine to influence the developing child from birth
-
Association For Prenatal & Perinatal Psychology and Health, APPPAH, founded in 1983.
Centre of natural neuroscinces NI H- Dr Brian G Dias and Dr Kerry Ressler stated 'We have a mind that is a composite of our experiences, our ancestors experiences and what we are taught within the womb. Each generation tells the next to unconsciously avoid what is unfamiliar and fearful Such a phenomenenmay contribute to the etiology and potential transgenerational transmission of neuropsychiatric disorders , phobias and anxiety.'
Studies
-
Dutch Hunger Winter 1998 – Susser
- - Suggests debilitating effects on nervous system due to famine exposure in utero leading to increased psychiatric risk( schizophrenia)
- Subsequent work in China in 2008- ST CLAIR gave similar results
-
Costello et al 2007
- - Population sample of 1400 boys and girls b/w 9-16 yrs in N.Carolina ( who had some adverse situation prenatally)
- - Adolescent depression 4 times higher in girls who were LBW 7 times higher in boys who were any birth wt
- - The rate of depression increased with additional adverse situation Possible alteration of physiological responses to stress involving the HPA axis
WOMB : A CLASSROOM
UTERUS : SENSORY PLAYGROUND

Fetal Senses Touch
THE FIRST SENSE TO DEVELOP
-
BEFORE 8 WEEKS – MOVEMENTS TO AVOID THE TOUCH OF A HAIR ON THE CHEEK;
-
10 W – SENSIBILITY IN THE GENITAL AREA;
-
11 W– PALMS
-
12 W – SOLES;
-
17 W - ABDOMEN AND BUTTOCKS;
-
32 W – WHOLE BODY IS SENSITIVE TO THE SOFT TOUCH OF A HAIR
FETAL SENSES TASTE AND SMELL
11 - 15 W – NOSE DEVELOPS, ODOURS BECOME AVAILABLE IN THE FLUIDS BATHING THE NASAL CAVITY
-
14 W – THE STRUCTURES OF TASTE ARE COMPLETED – SWALLOW MORE WITH SWEET TASTES
-
120 odours in amniotic fluid
Changes in FHR and breathing movement when mother drank coffee ( caff vs decaff)
Newborns are drawn to the odour of breastmilk though they have no previous experience with it
MORE CHANCES OF EARLY COMMUNICATION AND EDUCATION. FOOD PREFERENCES (COMMON AND LEARNED).
Vivette Glover: Imperial college , London
"The newborn when it hears music that its has heard when it was still in the womb eats more, sleeps more and cries less– not because they have received any special treatment but because powerful links were created through love and music"
"Sleep better , are more alert to their environment and surroundings and are far more content than who did not receive any prenatal stimulation"
Thomas Verny, Rene Vande Carr
Children who are “bathed” in music do better in maths and reading
Janellen H. : univ of chicago- Musica Prenatal, scientific discoveries
Fetal Learning
Learning and memory are interlocked EVIDENCE
-
Twins develop habits and gestures at 20wks
-
Parents – Kick game
-
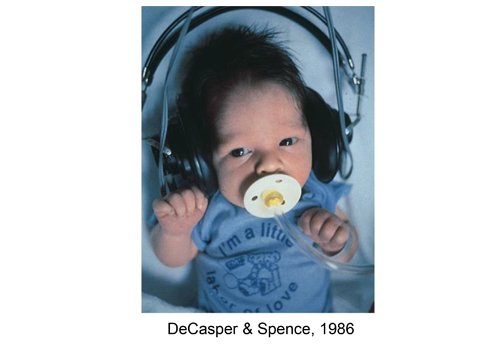
Mothers read The Cat in a Hat by Dr. Seuss, 2x/day for last 1½ months of pregnancy
-
Method: Changes in rate of sucking turned on or off a tape recorder of mother reading (half read that story, the other half another story)
-
Finding: Infants modified their rates of sucking in the direction that produced the familiar story
-
-
Babies learn their native language before birth
-
Traumatic experiences in the NICU
-
Babies learn their mothers emotional state Australian study- 20mt film segment
Newer concepts- Prenatal parenting (cont)
-
Parents pass more than genes to their offspring
-
Child may be inflicted with specific genetic defects , degree of defect’s expression is highly variable
-
Maternal effects add a powerful avenue
-
Material content- nutrition, toxins, smoking, alcohol, drugs e
-
Information content
-
Perceived attitudes about life
-
Mother emotions fear ,anger, love, hope can biochemically alter gene expression MOA
-
-

