ANTENATAL SCREENING
ANTENATAL SCREENING
EXPERT GROUP
- DR NARENDRA MALHOTRA
- DR MALA ARORA
- DR RANJANA KHANNA
- DR ABHA RANI SINHA
- DR PRAGYA MISHRA
- DR NAVNEET MAGON
- DR GANPAT SAWANTA
Reference Material
- New WHO guidelines on antenatal care – Systematic review BJOG 2016;123:519-28
- Guidelines by Government of western Australia
- SOGC guideline on Prenatal Screening
- RCOG / NICE Guidelines
Why Screen ?
WHY SCREEN ?
- Triage mothers to High Risk & Low Risk
- Prevent Maternal Complications
- Screen the fetus for
- Chromosomal errors
- Structural Defects
- Growth abnormalities
- Decide the time and mode of safe delivery
THE PYRAMID OF ANTENATAL CARE
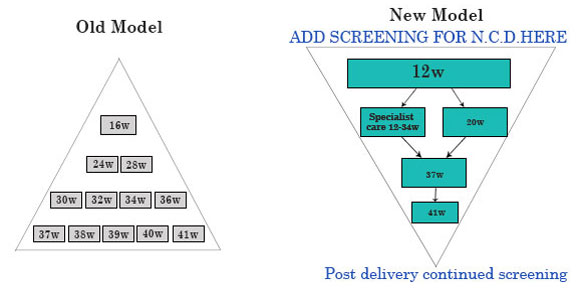
Routine Antenatal Care 1990s....
Early scan to diagnose pregnancy & dating
Fetal defects
22-24 wks
Anomaly scan
Routine Antenatal Care 2005
11-14 wks
Fetal defects
20-23 wks
P I P I P
The great Ob syndrome
Routine Antenatal Care 2010
11-13 +6 wks
Fetal defects Chemical markers Major Cardiac defects Uterine artery Doppler
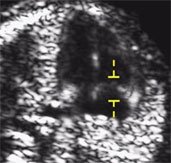
20-23 wks Anomaly scan
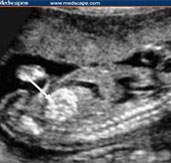
FOGSI OLD CHECK LIST OF 2009,MODIFIED IN 2017 AT FOGSI T.O.G.

FIRST TRIMESTER
FIRST TRIMESTER
Body Mass Index – If high
- Prevent further weight gain
- Institute Life style modifications
- Medical Therapy – Metformin
- Nutrition Therapy – High fibre diet
- Daily Exercise
- Prepare for safe delivery
General Examination
- Heart – Murmurs
- Lungs – Rhonchi
- Breast – Lumps / Nipples
- Abdomen – Scars / Lumps
- Per Speculum – Discharge / Polyp / Erosion LBC / HPV
- Anus – Sentinel Pile
Blood Pressure
- Hypertension – BP in both arms Sitting position Dissappearance of korotkov
- Hypotension – increase sodium/ potassium intake
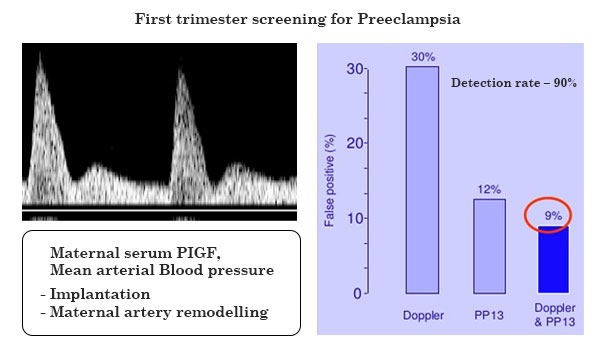
- Screening test for PIH
- Placental Growth Factor (PlGF)
- S Flt
- s endoglin
- Uterine artery doppler flow indices
Screening for Anaemia
- Complete Blood count
- Peripheral Smear
- If Microcytic Hypochromic
- Iron studies – Ferritin / Total Iron / TIBC
- Haemoglobin Electrophoresis
- If Normocytic / Macrocytic
- Serum Vitamin B12
- Serum / Red cell Folate
- Reticulocyte count
Blood group & Rhesus Antibodies
- If Rhesus Negative
- Partners Blood group – If negative –
- If positive – Indirect Coombs test
- If positive – Cordocentesis & fetal blood transfusion with Rh negative blood at periodic intervals
- Deliver at 34 weeks
Endocrine Screening
- Thyroid function test
- If abnormal, thyroid antibodies
- In PCO – screen for GDM early (HbA1C)
- If galactorrhea – Prolactin
- Serum Vitamin D
- Relaxin ?
Infection Screen
- Complete blood count /ESR
- Rubella antibodies
- Urine routine & microscopy
- Mid stream urine culture
- High Vaginal / Endo cervical swab /Wet Prep / Vaginal pH / Chlamydia antibodies (SOLVS + FVU PCR)
- HIV / Hep B / Hep C / VDRL
Biochemical Screening
First trimester screening (10 - 13 weeks + 6 days)
PAPP - A
Free beta HCG
Second trimester screening (15 - 22 weeks)
Triple Test
- MSAFP
- uE3
- hCG
Quadruple Test
- Inhibin
Various Integrated screening in strategies (1st and 2nd trim)
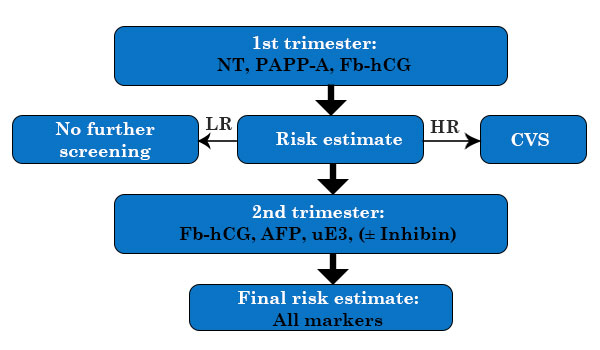
Main strategies:
- Fully Integrated
- Step-wise sequential
- Contingent screening
First trimester screening
Non Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
- NIPT – 9 weeks onwards
- At least 4% fetal fraction to be identified
- Twin Pregnancy – confusing results
- Vanishing twin – confusing results
- If positive – CVS / Amniocentesis
CVS
- 11-14 weeks
- Transcervical
- Check for chorionic villi under microscope
- Risk of miscarriage 1%
- Need is obviated now due to NIPT
Amniocentesis
- 15-18 weeks
- Risk of miscarriage < 1%
- To confirm diagnosis in positive integrated screen and/or positive NIPT
- To screen known carriers for chromosomally abnormal fetus
FIRST TRIMESTER SCREENING FOR CHROMOSOMAL ANOMALIES
FIRST TRIMESTER
Screening in the 1st trimester
- Time window: 8 - 14 weeks
- Ultrasound Marker:
- NT
- Biochemical markers:
- PAPP-A
- Fb-hCG
- Marker combination:
- Combined test: NT, PAPP-A, Fb hCG
Screening for Trisomy 21 at 11- 14 weeks
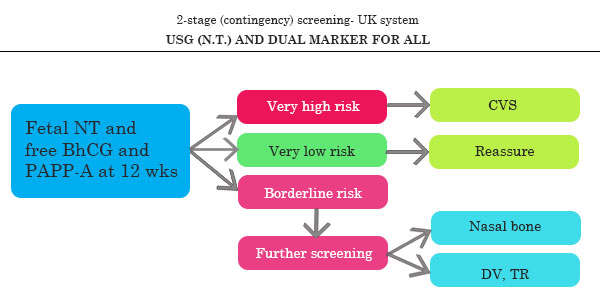
Screening for Trisomy 21 at 11- 14 weeks for India
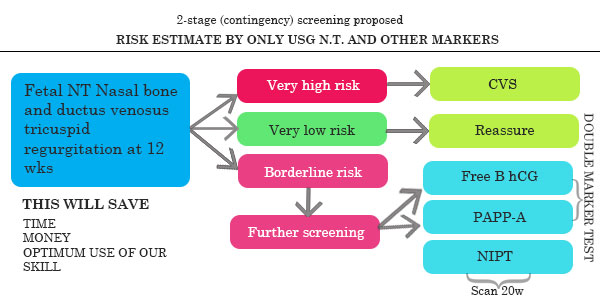
Integrated 1st and 2nd trimester screening
First trimester
- MA + NIPT(OPTIONAL)
- Dual Marker
- NT + NB + TR + DV
Second trimester
- Quad Marker
- Genetic Sonogram
DR – 97%
FPR – 2.5%
CONTINGENT SCREEN
SO PROPOSAL IS INDIAN CONTINGENT SCREEN OR INTEGRATED FIRST AND SECOND TRIMESTER SCREEN
COMBINED FIRST TRIMESTER SCREEN FOR RISK ESTIMATE...
FOLLOWED BY COMBINED 2ND TRIMESTER RISK SCREENING
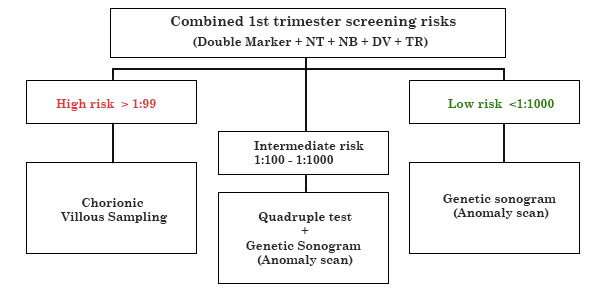
Combined 1st trimester screening risks
Combined 2nd trimester screening
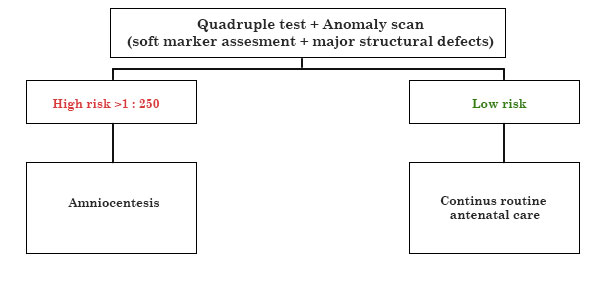
COMBINED SCREENING & RISK ESTIMATION IN FIRST TRIMESTER
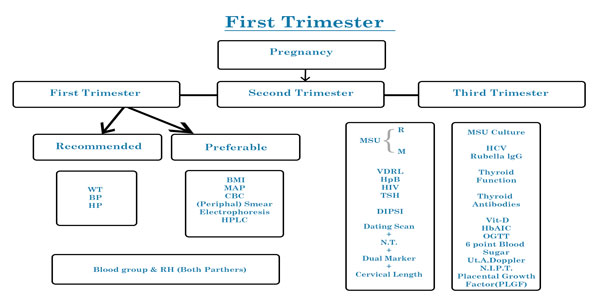
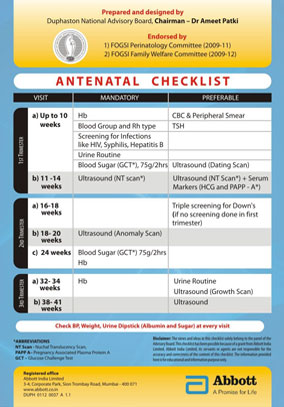
ANTENATAL CHECKLIST
| First Trimester | Recommended | Preferable |
|---|---|---|
| weight | BMI | |
| Blood pressure | Mean Arterial Pressure | |
| Haemoglobin | Complete blood count/ Peripheral smear / Hb Electrophoresis / HPLC | |
| Blood group ABO & Rh (both partners) | ||
| Urine routine | MSU culture | |
| VDRL/ Hep B / HIV | HCV / Rubella IgG | |
| TSH | Thyroid function test / Thyroid Antibodies Vitamin D | |
| DIPSI test 75gms 2 hours blood sugar | Hb A1C / OGTT/ 6 point blood sugar test | |
| Dating scan + NT Double marker (free beta HCG + PAPP A 1 ) Contingent Screen 2 | Cervical length Uterine artery Doppler NIPT Placental Growth Factor (PLGF) | |
| Per speculum exam | Pap Smear, Bacterial vaginosis & Chlamydia screen |
LOW LEVELS PREDICT PRE ECCLAMPSIA
LOW RISK NO FURTHER TEST (1 : 1000)
INTERMEDIATE RISK (100 : 999) TO PROCEED TO SECOND TRIMESTER SCREENING VS NIPT HIGH RISK (1 : 99) TO GO FOR CVS / NIPT
SECOND TRIMESTER SCREENING
SECOND TRIMESTER SCREENING
CERVICAL LENGTH SCREENING
CERVICAL LENGTH SCREENING ROUTINE TO PREVENT PRETERM LABOUR AND FOR GUIDELINE FOR CX STITCH
- ASYMPTOMATIC SINGLETON PREGNANCY A TVS CL <25 MM IN SECOND TRIMESTER
- SCREEN AT 11-13 WEEKS AND THEN AT 22-22 WEEKS
RECENT EVIDENCE SAYS CX STITCH DOES NOT HELP AND PROGESTERONE MAY BE THE ONLY TREATMENT OPTION HERE.ROUTINE MCDONALD STITCH PRACTISE SHOULD BE INDIVIDUALISED
SECOND TRIMESTER
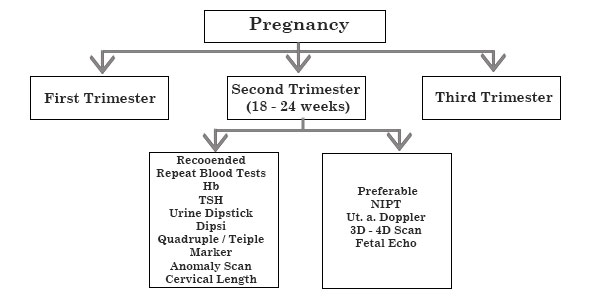
ANTENATAL CHECKLIST
| Second Trimester | Recommended | Preferable |
|---|---|---|
| 18-24 weeks | Repeat bloods (Hb / blood sugar / TSH) & urine test as indicated | |
| Quadruple OR Triple marker | NIPT | |
| Anomaly scan | 3D/4D scan/ Fetal Echo Uterine artery Doppler | |
| Cervical length | ||
| DIPSI screen 75 gms 2 hour blood sugar | 6 Points Blood Sugar HbA1C |
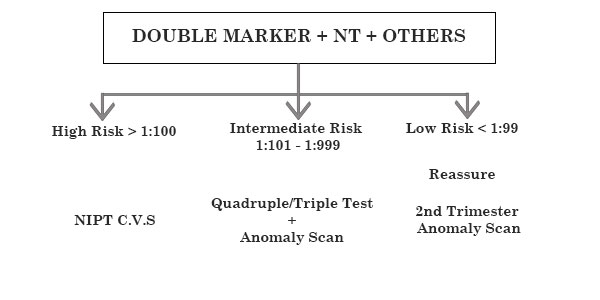
Sequential Screening
- Quadruple marker – 15-18 weeks
- NIPT 9 week onwards
- Amniocentesis – 15 week onwards
COMBINED 2ND TRIMESTER SCREENING
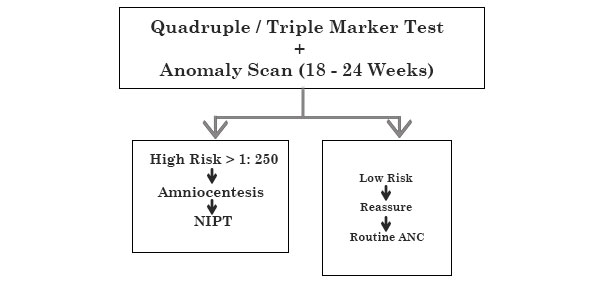
ANOMALY SCAN
ANOMALY SCAN
Screening for GDM
- HbA1C
- DIPSI one step screen 75 gms 2 hour
- Cut off of 140 mg/dl
- At 24 to 28 weeks
- Repeat at 32 weeks in high risk women i.e Polyhydramnios / previous GDM / Parents & siblings diabetic
Screening for PIH
- Blood Pressure
- Water Retention – edema / rapid weight gain
- Micro albuminuria
- Spot test – Urine Protein /Creatinine ratio
- Ratio of PlGF / sFlt
- LDH raised in HELLP Syndrome
- Renal artery doppler
Vaccination
- Tetanus Toxoid – ONE DOSE
- Tdap –SECOND DOSE AT 24 WEEKS
- Influenza vaccine 24 weeks onwards
- hpB can be given if not immunised
- Targetted Vaccine in case of travel to endemic areas
- Post partum – HPV vaccine
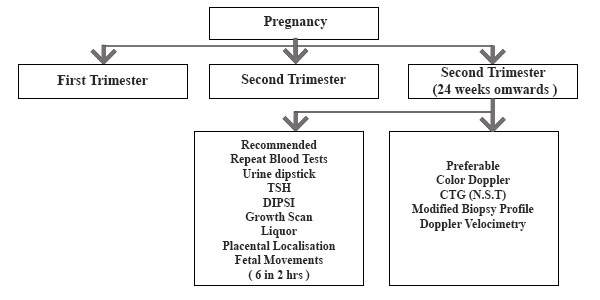
THIRD TRIMESTER SCREEN
- Hb Haemoglobin
- TSH Thyroid stimulating hormone
- HbA1C Haemoglobin A1C
- Scan,
- NIPT Non invasive prenatal testing
- Plasma protein A
- PlGF Placental growth factor
- HCV Hepatitis C virus
- HIV Human Immune defeciency virus
- Chromatography
- GCT- Glucose Challenge Test
- OGTT Oral glucose tolerance test
- NT Scan- Nuchal Translucency
- PAPP A- Pregnancy Associated
- VDRL Venereal disease reference
- Hep B hepatitis B virus HPLC high performance liquid
THIRD TRIMESTER SCREEN
| Third Trimester | Recommended | Preferable |
|---|---|---|
| 24 weeks onwards | Repeat DIPSI Screen TSH/Hb/Urine | HbA1C |
| Growth scan with liquor volume & placental localisation | Fetal Doppler velocimetry | |
| Fetal movement count (6 in 2 hours) | CTG (NST) Modified biophysical Score Doppler velocimetry |
THIRD TRIMESTER
INFECTION SCREEN
- GBS – Is routine screening required prior to delivery ?
- Pelvic assessment – Does it improve your decision for normal delivery ?
- Pelvic relaxation techniques / exercises like walking / squatting / butterfly
NON USG SCREENING FOR FETAL WELL BEING
CARDIOTOCOGRAPHY
- Non Stress test vs Oxytocin Stress test
- When to start ? Post viability period 30 weeks
- How often to do ? Once a week
- What are the omnious signs –
- Lack of BTB variation
- Variable deaccelerations of cord compression
- Late deacceleration of fetal hypoxia
- Supplement with ST waveform analysis
- Fetal cord blood pH during labour
KICK CHART
Recording
- Every kick / roll is 1 movement
- Count 10 movements everyday
- Should be around 6 in 1 hour
- If < 6 movements in 2 hours
- Call doctor & come for CTG / USS assessment
How do I count my baby’s movements?
- Get into a comfortable position – lying on your side or sitting. Place one or both of your hands on your abdomen.
- Count each time that you feel your baby move. If you feel many movements all at once, count each movement that you feel.
- Write down the date and the time that you start counting on the fetal movement chart
- Stop counting when you have counted 6 movements
- Write down the time you stopped counting.
- Do not count for more than 2 hours
Count your baby’s movements once a day. You should feel 6 or more movements in 2 hours.
What if I don’t feel 6 movements in 2 hours?
If you count fewer than 6 movements in 2 hours do not wait. Go to the hospital or birthing unit.
Your baby’s heart rate and movements will be checked using a fetal monitor. This is called a non-stress test or NST.
If you live too far from a hospital or birthing unit, immediately contact your health care provider for advice.
About baby’s movements
An active baby is usually a healthy baby. You will feel your baby stretch, kick, roll and turn every day. Some babies are more active than others. All babies have periods of sleep during which they are not as active. You will get to know your baby’s pattern of movements and when your baby is most active.
You should feel your baby’s movements throughout the day, each day from 28 weeks of pregnancy until the baby is born.
When during my pregnancy should I count my baby’s movements?
Your health care provider may ask you to count your baby’s movements once every day.
If you think there is a decrease in your baby’s movements this is an important sign that your baby may not be well. Count your baby’s movements to be sure that you feel at least 6 movements in 2 hours.
Reference:
Society of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of Canada (2007).
Fetal Health Surveillance : Antepartum and Intrapartum Consensus Guideline. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Canada. 29(9).
FETAL MOVEMENT COUNT CHART

TWEAK Screening for alcoholism
- T – Tolerance (No of drinks one can hold)
- W- Worry about drinking
- E – Eye opener
- A - Amnesia
- K/C – Cut down on drinking
- To screen for fetal alcohol syndrome
- Antepartum fetal surveillance is the assessment of fetal well being in utero before the onset of labor
- Early detection of fetus at risk so that timely management to prevent further deterioration
- Also find out normal fetuses and avoid unnecessary interventions
- Very high negative predictive value
- Very low positive predictive value
FETUS AT RISK
- PRE TERM
- POST TERM
- IUGR
- THICK MECONIUM WITH SCANTY FLUID
- INTRAUTERINE INFECTION
- INTRAPARTUM BLEEDING
FETUS AT RELATIVE RISK
- INJUDICIOUS USE OF OXYTOCIN
- EPIDURAL IN A CASE WITH SOME COMPROMISE
- DIFFICULT INSTRUMENTAL DELIVERY/ MACROSOMIA/ MALPRESENTATION
- ACUTE EVENTS (CORD PROLAPSE, ABRUPTION, SCAR RUPTURE)
- SUSPICIOUS/ ABNORMAL ADMISSION TEST
Admission assessment Are any risk factors present?
Maternal problems
- Previous LSCS
- Pre-eclampsia
- Post-term pregnancy (>42 weeks)
- Prolonged membrane rupture (>24 hours)
- Induced labour
- APH
- Other maternal disease
Fetal problems
- Growth restriction
- Prematurity
- Oligohydramnios
- Abnormal dopplers
- Multiple pregnancy
- Meconium stained liquory
- Breech presentation
INDICATION OF FETAL SURVEILLANCE
Maternal conditions
- Hypertension
- Diabetes mellitus
- Heart Disease
- Chronic renal disease
- Acute febrile illness
- Pneumonia /asthma
- Epilepsy
- Collagen vascular disease
- Sickle cell disease
- Antiphospholipid syndrome
- Drug Abuse
- Fetal conditions
- Fetal growth restriction
- Rh isoimmunisation
- Fetal Cardiac arrythmia
INDICATION OF FETAL SURVEILLANCE
Maternal conditions
- Hydrops fetalis
- Fetal infections
- Pregnancy Related Conditions
- Preeclampsia
- Multiple pregnancy
- Post term pregnancy
- Decreased fetal movements
- Abnormal placentation
- Oligohydramnios
- Polyhydramnios
- Unexplained stillbirth in a previous pregnancy
- Cholestasis of pregnancy
- PROM
- Poorly controlled Gestational Diabetes mellitus
The Various Methods of Antepartum Fetal Surveillance
- Clinical assessment by uterine growth
- Fetal movement count by the mother
- Ultrasound for fetal growth
- Non stress test and cardiotocography
- Vibroacoustic stimulation test
- Contraction stress test
- Nipple stimulation test
- Biophysical profile
- Modified biophysical profile
- Doppler studies
- Fetal lung maturation studies
- Placental grading
Check list made a few years back....NOW TO BE MODIFIED
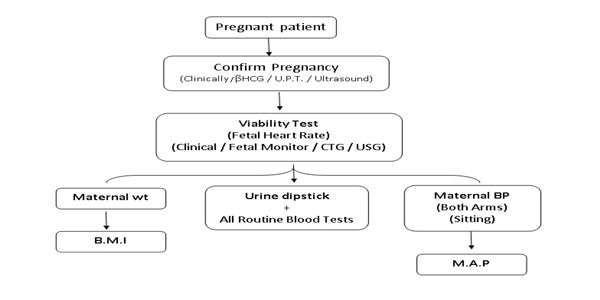
SCREENING IN PREGNANCY
At booking (Recommended 3ANC) [Preferable 5]
General Physical exam Heart / Lungs / Breast / Abdomen
In all trimesters
- Maternal weight /BMI
- Blood Pressure / Mean Arterial Pressure
- Urine dipstick (albumin sugar)
ANTENATAL CHECKLIST
| First Trimester | Recommended | Preferable |
|---|---|---|
| weight | BMI | |
| Blood pressure | Mean Arterial Pressure | |
| Haemoglobin | Complete blood count/ Peripheral smear / Hb Electrophoresis / HPLC | |
| Blood group ABO & Rh (both partners) | ||
| Urine routine | MSU culture | |
| VDRL/ Hep B / HIV | HCV / Rubella IgG | |
| TSH | Thyroid function test / Thyroid Antibodies Vitamin D | |
| DIPSI test 75gms 2 hours blood sugar | Hb A1C / OGTT/ 6 point blood sugar test | |
| Dating scan + NT Double marker (free beta HCG + PAPP A 1 ) Contingent Screen 2 | Cervical length Uterine artery Doppler NIPT Placental Growth Factor (PLGF) | |
| Per speculum exam | Pap Smear, Bacterial vaginosis & Chlamydia screen |
LOW LEVELS PREDICT PRE ECCLAMPSIA
LOW RISK NO FURTHER TEST (1 : 1000)
INTERMEDIATE RISK (100 : 999) TO PROCEED TO SECOND TRIMESTER SCREENING VS NIPT HIGH RISK (1 : 99) TO GO FOR CVS / NIPT
| Second Trimester | Recommended | Preferable |
|---|---|---|
| 18-24 weeks | Repeat bloods (Hb / blood sugar / TSH) & urine test as indicated | |
| Quadruple OR Triple marker | NIPT | |
| Anomaly scan | 3D/4D scan/ Fetal Echo Uterine artery Doppler | |
| Cervical length | ||
| DIPSI screen 75 gms 2 hour blood sugar | 6 Points Blood Sugar HbA1C |
| Third Trimester | Recommended | Preferable |
|---|---|---|
| 24 weeks onwards | Repeat DIPSI Screen TSH/Hb/Urine | HbA1C |
| Growth scan with liquor volume & placental localisation | Fetal Doppler velocimetry | |
| Fetal movement count (6 in 2 hours) | CTG (NST) Modified biophysical Score Doppler velocimetry |
- Hb Haemoglobin
- TSH Thyroid stimulating hormone
- HbA1C Haemoglobin A1C
- Scan,
- NIPT Non invasive prenatal testing
- Plasma protein A
- PlGF Placental growth factor
- HCV Hepatitis C virus
- HIV Human Immune defeciency virus
- Chromatography
- GCT- Glucose Challenge Test
- OGTT Oral glucose tolerance test
- NT Scan- Nuchal Translucency
- PAPP A- Pregnancy Associated
- VDRL Venereal disease reference
- Hep B hepatitis B virus HPLC high performance liquid
FIRST TRIMESTER


COMBINED SCREENING & RISK ESTIMATION IN FIRST TRIMESTER

SECOND TRIMESTER

Combined 2nd trimester screening

THIRD TRIMESTER

| Third Trimester | Recommended | Preferable |
|---|---|---|
| 24 weeks onwards | Repeat DIPSI Screen TSH/Hb/Urine | HbA1C |
| Growth scan with liquor volume & placental localisation | Fetal Doppler velocimetry | |
| Fetal movement count (6 in 2 hours) | CTG (NST) Modified biophysical Score Doppler velocimetry |
- Hb Haemoglobin
- TSH Thyroid stimulating hormone
- HbA1C Haemoglobin A1C
- Scan,
- NIPT Non invasive prenatal testing
- Plasma protein A
- PlGF Placental growth factor
- HCV Hepatitis C virus
- HIV Human Immune defeciency virus
- Chromatography
- GCT- Glucose Challenge Test
- OGTT Oral glucose tolerance test
- NT Scan- Nuchal Translucency
- PAPP A- Pregnancy Associated
- VDRL Venereal disease reference
- Hep B hepatitis B virus HPLC high performance liquid
Abbreviations
- Hb Haemoglobin
- GCT- Glucose Challenge Test
- TSH Thyroid stimulating hormone
- OGTT Oral glucose tolerance test
- HbA1C Haemoglobin A1C
- NT Scan- Nuchal Translucency Scan,
- NIPT Non invasive prenatal testing
- PAPP A- Pregnancy Associated plasma protein A
- PlGF Placental growth factor
- VDRL Venereal disease reference
- HCV Hepatitis C virus
- Hep B hepatitis B virus
- HIV Human Immune defeciency virus
- HPLC high performance liquid chromatography