Adbhut Matrutva
The third trimester algorithm

Dr S.SHANTHA KUMARI
M.D. D.N.B. FICOG FRCPI (Ireland)
Consultant –Yashoda Hospitals, Hyderabad
PROFESSOR OBGYN
CHAIRPERSON ICOG 2018
CONSULTANT YASHODA HOSPITAL
ICOG SECRETARY 2015 -2017 (Indian College of Obstetricians & Gynaecologists)
Member FIGO working Group on Violence Against Women
VICE PRESIDENT FOGSI 2013
ICOG GOVERNING COUNCIL MEMBER
IAGE MANAGING COMMITTEE MEMBER
NATIONAL CORRESPONDING EDITOR FOR JOGI
ORGANIZING SECRETARY AICOG 2011CHAIRPERSON MNNRRC 2008
Third trimester of pregnancy
Week 28 – labour/delivery
Care During Pregnancy





"Algorithmic approach": third trimester
Proceed step by step in a logical manner to continue antenatal care from second trimester till labour/delivery
Step 1 : taking stock
- Review notes till the second trimester
- Check routine investigations check list
- Review risk factors
- Plan further antenatal visits and tests
- Plan further care …..

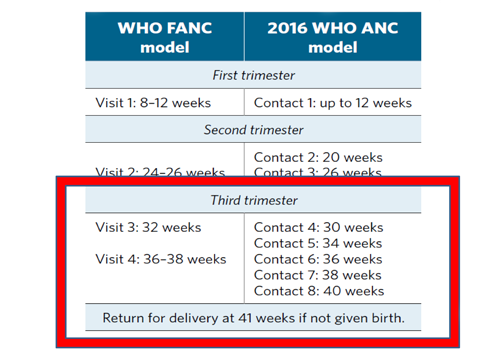
WHO Guideline on Antenatal Care (2016)
Overview
Reproductive Health and Research (RHR)
Nutrition for Health and Development (NHD)
Maternal, Newborn, Child and Adolescent Health (MCA)


Antenatal care is critical

Through timely and appropriate evidence-based actions related to health promotion, disease prevention, screening, and treatment

- Reduces complications from pregnancy and childbirth
- Reduces stillbirths and perinatal deaths
Women’s views

Women want a
Positive Pregnancy Experience
from ANC
- A healthy pregnancy for mother and baby (including preventing or treating risks, illness and death)
- Physical and sociocultural normality during pregnancy
- Effective transition to positive labour and birth
- Positive motherhood (including maternal self-esteem, competence and autonomy)
Medical care; relevant and timely information; emotional support and advice
2016 WHO ANC model

Contact versus visit
- The guideline uses the term 'contact' - it implies an active connection between a pregnant woman and a
health care
provider that is not implicit with the word 'visit'.
- – quality care including medical care, support and timely and relevant information
- In terms of the operationalization of this recommendation, 'contact' can take place at the facility or at
community
level
- – be adapted to local context through health facilities or community outreach services
- 'Contact' helps to facilitate context-specific recommendations
- – Interventions (such as malaria, tuberculosis)
- – Health system (such as task shifting)

IMMUNIZATION IN PREGNANCY
ROUTINE VACCINES: SAFE DURING PREGNANCY
- Tetanus
- Influenza
- Hepatitis B
- Meningococcal
- Rabies
Special considerations ; pneumococcal vaccine, typhoid, cholera, hepatitis A, Yellow fever, Japanese encephalitis, polio.
CONTRAINDICATED- Live attenuated vaccines Measles, mumps, Rubella, Varicella, BCG Oral polio

Influenza
-
Killed virus preparation with annually adjusted antigenic makeup.
-
Current Canadian recommendations advocate universal immunization of pregnant women against influenza in second or third trimester of pregnancy.
-
Another reason for immunization in pregnancy is the protection of the newborn after birth, which can be accomplished with passive immunity (transfer of maternal antibodies). Further, the most common way for infants to acquire influenza is from household contacts, so immunization of the mother can prevent her from acquiring influenza and potentially passing it on to her child.
-
Trivalent inactivated influenza vaccine (TIV),live attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV),recombinant quadrivalent vaccines are available in India.
-
TIV is annual, single IM dose of 0.5 ml also known as flu shot(H1N1,H3N2,influenza B)
-
LAIV is administered by the intranasal route is approved for use in adults upto 50 years of age. Evidence recommends people at high risk for influenza related complication.
-
Recombinant quadrivalent vaccine is given, intradermal 0.5ml single dose. saftey in pregnancy is under trial.
Committee Opinion

- Obstetric care providers should administer the tetanus toxoid, reduced diphtheria toxoid, and acellular pertussis (Tdap) vaccine to all pregnant patients during each pregnancy, as early in the 27–36-weeks-of-gestation window as possible.
- Pregnant women should be counseled that the administration of the Tdap vaccine during each pregnancy is safe and important to make sure that each newborn receives the highest possible protection against pertussis at birth.
- Obstetrician–gynecologists are encouraged to stock and administer the Tdap vaccine in their offices.
- Partners, family members, and infant caregivers should be offered the Tdap vaccine if they have not previously been vaccinated. Ideally, all family members should be vaccinated at least 2 weeks before coming in contact with the newborn.
- If not administered during pregnancy, the Tdap vaccine should be given immediately postpartum if the woman has never received a prior dose of Tdap as an adolescent, adult, or during a previous pregnancy.
- There are certain circumstances in which it is appropriate to administer the Tdap vaccine outside of the 27–36-weeks-of-gestation window. For example, in cases of wound management, a pertussis outbreak, or other extenuating circumstances, the need for protection from infection supercedes the benefit of administering the vaccine during the 27–36-weeks-of-gestation window.
- If a pregnant woman is vaccinated early in her pregnancy (ie, before 27–36 weeks of gestation), she does not need to be vaccinated again during 27–36 weeks of gestation.
Third trimester checklist
What has been done
- Booking tests
- ANC notes
- Screening tests for anemia, infections, pre eclampsia, GDM and fetal anomalies/aneuploidies
- TT immunisation
- Familiarise with important past history / familial health issues
Plan for What needs to be done

Third trimester algorithm : By 28 weeks
- Measure Symphisio fundal height
- Hemoglobin – 28wks – second check for anemia
- Red cell antibodies
- Indirect Coomb’s test for the Rh negative
- OGTT – second check for GDM
- BP measurements, proteinuria
- Offer opportunity to ask questions and clarify doubts
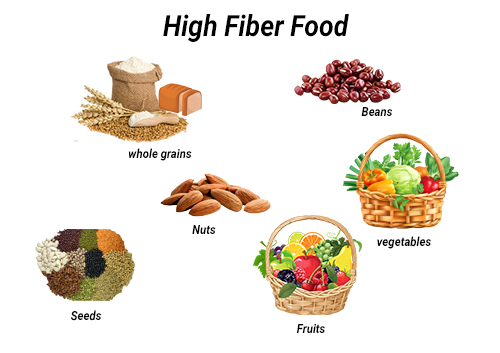
Nutrition in third trimester

-
Fresh fruits /vegetables : "5-a-day"
-
Carbohydrates – whole grain varieties at every meal
-
Low fat dairy products :2-3 times a day
-
Proteins: varieties of protein rich foods: 2 times a day

My Pregnancy Plate



DIET IN PREGNANCY



Yoga in third trimester

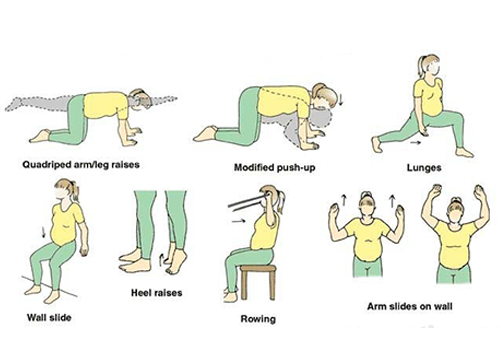
-
Relieves Backache
-
Helps in increasing physical wellness – posture and balance
-
Increases positive endorphins – good mood
-
Meeting people
-
Making friends
-
Peer groups
-
Better diet habits

Exercises During Pregnancy


COSMETIC CARE

-
Hyperpigmentation
-
Frontoparietal thinning of hair due to increase in androgens
-
Telogen effluvium- postpartum, diffuse shedding
-
Striae : abdomen, breats,thighs (mechanical stretching and increased estrogen, relaxin, adrenocortical hormones)
CLEANLINESS
Personal Hygiene prevents acquiring infection and also from transmittibg to the baby

Wash your hands with soap and water before every meal and after attending toilet.

Clip your nails regularly

Have a bath daily
Dental hygiene
PREPARING FOR DELIVERY
STAGES OF LABOUR
-
I Stage : Early labor and active labor. Early contractions that are irregular and last less than a minute.(last from a few hours to days). active contractions that are regular and last about a minute. Once active contractions begin - need to head to a hospital or birthing center.
-
II Stage: lasts through the actual birth. During the second stage,cervix is completely dilated and baby travels down and out of the birth canal.
-
III Stage: occurs after baby is born. Contractions continue until the placenta is delivered out of birth canal.

Third trimester algorithm : 32-34 weeks
-
Measure symphysio fundal height
-
Plot on gravidogram
-
Check BP – proteinuria
-
Fetal growth scan as indicated
-
Placental localisation scan as indicated(based on earlier suspicion of previa/accrete etc)
-
Review earlier tests and discuss further care plan with the pregnant woman – allow her to ask questions and clarify doubts
-
Identify women with need for additional support
General discomfort
-
Physically challenging to handle the increased "weight of pregnancy"
-
Sleeplessness
-
Irritability
-
Tender loving care
-
Positive motivation by spouse, peers and family

Third trimester algorithm : 36-40 weeks
-
Measure symphysio fundal height
-
Plot on gravidogram
-
Check BP – proteinuria
-
Check fetal position
-
Consider ECV for breech presentation
-
Refer the women with placenta previa/accrete to appropriate centres
-
Discuss further care plan with the pregnant woman – allow her to ask questions and clarify doubts
Third trimester algorithm : 40 weeks - delivery
-
Measure symphysio fundal height
-
Plot on gravidogram
-
Check BP – proteinuria
-
Closer antenatal surveillance
-
Refer to district hospital if needed
-
Offer induction of labour
-
Discuss further care plan with the pregnant woman – allow her to ask questions and clarify doubts
FETAL KICK COUNT
MATERNAL PERCEPTION OF DECREASED FETAL COUNT MAY BE A RED FLAG SIGN FOR IMPENDING FETAL DISTRESS.
Fetal kick are appreciated for the first time at around 18-20weeks.
Fetal kick count is significant after 28weeks.
The DFMC requires pregnant women to begin a fetal movement count at a selected time each day, count 10 movements and record the elapsed time from the first to the tenth movement. Findings which would indicate possible danger to the fetus, and which should be reported immediately, include less than 10 movements in 12 hours; no perception of movement in an eight- hour period; a change in the usual pattern of fetal movement; or a sudden increase in violent fetal movements followed by complete cessation of movement.

kick count log

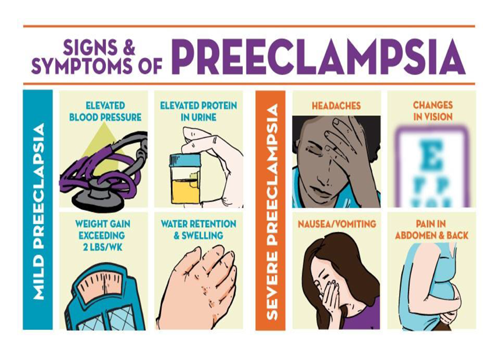
Danger Signs During pregnancy



WHAT ARE THE DANGER SIGNALS?
IF ANY OF THE FOLLOWING OCCUR – SEEK HELP IMMEDITALEY AND REACH HOSPITAL TO PRESERVE YOUR HRALTH AND LIFE
-
Severe abdominal pains or cramps
-
Generalised weakness, easy fatiguability and breathlessness
-
Vaginal bleeding
-
Convulsions
-
Excessive swelling of the feet,
-
blurring of vision,
-
severe and persistent headache
-
Decreased urine output
-
Fever
-
Sudden gush of fluid from the vagina
Danger Signs During pregnancy

Varginal Bleeding

Fits

Severe Abdominal Pain

Severe Headache

Very Pale

Fever
When to go to Hospital
-
Regular Contractions with intensity
-
SROM
-
Vaginal Bleeding
-
Changes in Fetal Movement ecpecially a in fetal movement as described in the Daily Fetal Movement Count
Overall wellbeing
-
Practicing empathy and effective listening as a health care provider
-
Address emotional wellbeing issues:
- Stop Worrying
- Communicating feelings and needs to others
- Partner compatibility


Working women : third trimester
-
Planning maternity leave
-
Traffic safety issues if driving to work
-
Emergency contact persons
-
Back up plan for sudden
GOI initiatives

PREPARING FOR BREAST FEEDING AND POST PARTUM PERIOD
Postpartum Problems Every Mom Should Know About

Caring For Tears Or An Episiotomy Wound
It is normal for vaginal wounds to take a few weeks to heal, but do watch out for signs of infection. If your wound becomes red, hot, or starts oozing pus see your OBGYN right away.
Breast Problems
Apply cold compresses and cabbage leaves on sore breasts, gently massage your breasts or even pump some milk. Lanolin soothes cracked and painful nipples.
Lochia-The 'Mother Of All Periods'
Seek medical help if you pass extremely large clots, bleed so heavily that you saturate a pad or more an hour, or your lochia smells foul.
Diastasis Recti
Wait until your healthcare provider gives you the green light to exercise, usually at the six-week postpartum checkup.
Baby Blues & Postpartum Depression
Did you know that between 70 and 80 percent of postpartum moms experience some mood swings or negative feelings after their baby's birth?
Uterine Problems
The Uterus needs to shrink back to its tiny non-pregnant size after labor and birth, and this might cause painful contractions. Your pelvic floor muscles will have weakened during pregnancy and birth, so it is best to start doing kegel exercises soon after you give birth.
Constipation And Hemorrhoids
Apply cold packs to the area to eqase swelling and pain. Herbal sitz baths combat hemorrhoids and vaginal tears.
BREAST FEEDING

-
Breastfeeding is one of the most effective ways to ensure child health and survival.
-
If every child was breastfed within an hour of birth, given only breast milk for their first six months of life, and continued breastfeeding up to the age of two years, about 800,000 child lives would be saved every year.

Advantages of Breastfeeding
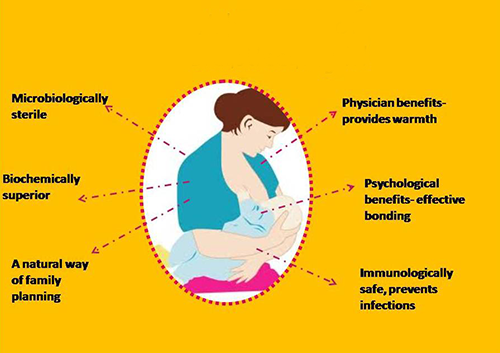
Benefits of Breastfeeding for the mother
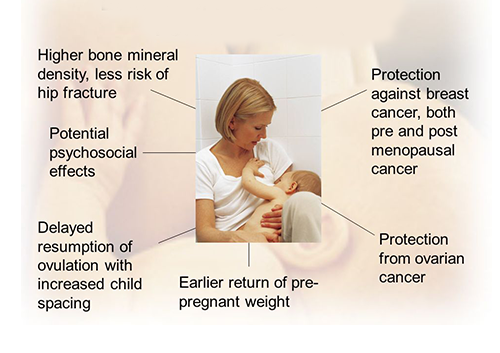
Risks of artificial feeding
-
Interferes with bonding
-
More diarrhoea and respiratory infections
-
Presistent diarrhoea
-
Malnutrition Vitamin A deficiency
-
More likely to die
-
More allergy and milk intolerance
-
Increased risk of some chronic diseases
-
Overweight
-
Lower scores on intelligence tests
-
May become pregant sooner
-
Increased risk of anaemia, ovarian and breast cancer

Successful Breastfeeding Poster
Benefits to the Breastfed Infant


It lessens the risk of being an obese later in life

Less chance of developing eczema

They are likely to die of SIDS

They have fewer ear infections

They have better vision

They have healthier brains

Protects your baby from infections and diseases

Less chance of diarrhoea and vomiting

Natural food designed for your baby

It makes nappies less smelly

They have better skin

It can give you great sense of achievement
What's In Breast Milk?
Breast milk is a unique combination of nutrients essential to a child's health
1% proteins, 87% water, 7% carbohydrates, vitamins-mineral-hormones 1%, fats 4%

Breastfeeding results in less days for parents breastfeeding satisfies baby's emontional needs

Better social development
SENSITIZATION AND CONNECTING WITH YOUR CHILD AND DOCTOR

-
The closeness of the parent-child connection throughout life results from how much parents connect with their babies, right from the beginning.
Third trimester:MUST DO
-
Breast feeding techniques
-
Preparation for labour and birth
-
Recognition of active labour
-
Care of newborn
-
Postnatal self care
-
Awareness of postnatal depression


Third trimester of pregnancy: Week 28 – labour/delivery
"Algorithmic approach": third trimester
Proceed step by step in a logical manner to continue antenatal care from second trimester till labour/delivery
