VACCINATION IN WOMEN
Prof Girija Wagh
NAME: GIRIJA WAGH
MD FICOG DIP IN GYN ENDOSCOPY...
Designation: PROFESSOR OBGYN
Organisation: Bharati Vidyapeeth University Medical College
Consultant Cloudnine Hospitals Pune
Director Girija Hospital & Fertility Center
Professional Brief & Awards:
- Trupta Umranikar Award for first in MD 1992 ,Pune Univ
- Anandibai Joshi Award for excellence in medical service
- Specialization : Maternal fetal Medicine ,Gyn Endoscopy
- Member of the Steering Committee World Organisation Gestosis
- Asst Coordinator National Eclampsia Registry
- Chairman Medical Disorders in Pregnancy Committee FOGSI 2013-16
- Joint Secretary FOGSI 2010


Vaccination is generally considered the purview of the pediatricians in the childhood and physicians in the adult context .
There are many vaccinations such as the rubella which need to be extended to the adolescent age group and hepatitis and HPV need to be considered in this age group .
In addition vaccinations during pregnancy such as the flu, tetanus,pertussis, chicken pox and diphtheria need to considered.
Vaccinations for pregnant women during pandemics need to be given special consideration.
Why vaccinate women ?
- Vaccination before during and after pregnancy helps protect women from serious infections .
- It can also help in improving the women’s health in general .
- It is an important preventable measure which should be adopted rationally

"IF You Educate a Man You Educate an Individua, but if You Educate a Nation."
- African Proverb


The best judge of whether or not a country is going to develop is how it treats its women. If it's educating its girls, if women have equal rights, that country is going to move forward. But if women are oppressed and abused and illiterate, then they're going to fall behind.
- Barack Obama -
- Ideally, all women should be up-to-date with their vaccinations before they become pregnant.
- It is known that approximately 50 percent of all pregnancies are unplanned
- it is important to keep women of reproductive age current with immunizations, regardless of whether they are actively trying to conceive.
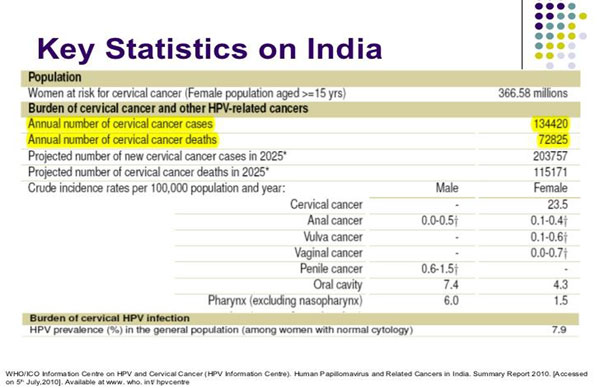
Key Statistics On India
Vaccination in the adolescent age group

Adolescent vaccination recommendations
- MMR (2),Hep B ,Hep A ,HPV, tetanus,diphtheria , influenza and VAR(2) catch up vaccination is recommended from 11 years onwards.
- Typhoid and cholera vaccination can be given seasonally.
VACCINES OF THE TEENAGE GIRL
- Catch up vaccinations for Hepatitis B, Tetanus, diphtheria acellular pertussis(Tdap),typhoid, Influenza, rubella and HPV are recommended in the adolescent age group.
- The medical history of prior affliction with these diseases should be elicited.
- Previous adverse effects of immunizations especially allergies should be noted.
FOGSI recommends
FOGSI recommends Rubella Vaccine to all adolescent girls as history of rubella infection is difficult to elicit.
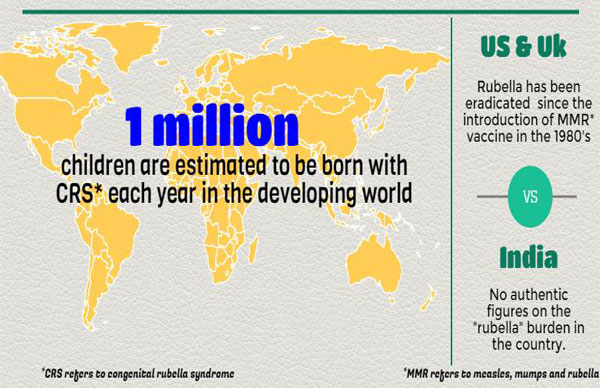
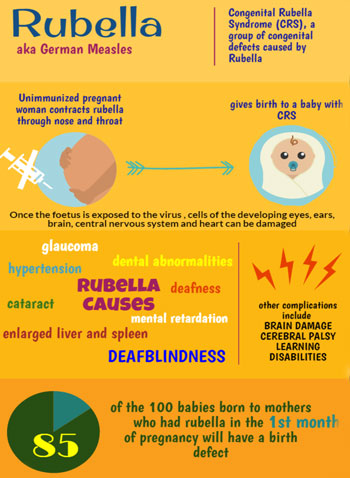
- This is to prevent the incidence of Congenital Rubella Syndrome (CRS) which occurs through vertical transmission if the woman is infected during the first 3 months of pregnancy.
- Antibody testing is not necessary before vaccination.
- Pregnancy should be avoided within three months of vaccination.
- However if pregnancy occurs within 4 weeks of vaccination there is a small chance of the fetus being born with CRS and usually follow and close monitoring with USG is advised instead of pregnancy termination .

HPV vaccination
HPV vaccine options
| Vaccine | Who is it for? | How many doses? | What infections does it prevent? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cervarix | Girls 9 to 26 years of age. | 3 | HPV types 16 and 18 (Which cause cancer). |
| Gardasil | Girls and boys 9 to 6 years of age. | 3 | HPV types 6, 11 (which cause genital warts), and HPV 16 and 18 (Which cause cancer). |
| Gardasil 9 | Girls ages 9 to 26; boys ages 9 to 15. | 3 | HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52, and 58 (which cause cancer), and HPV types 6 or 11 (which cause warts). |
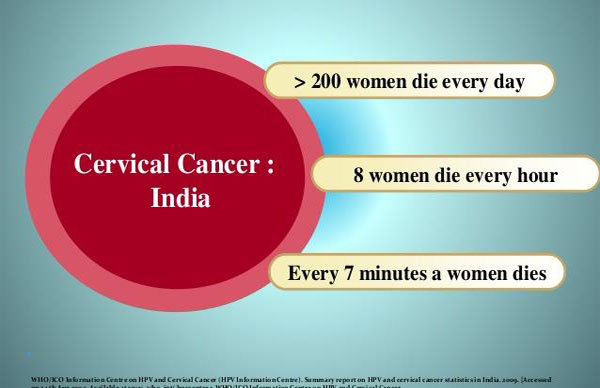
- FOGSI recommends HPV vaccination in all adolescents for protection against cancer cervix.
- This is best given as early as the age of 9 years or before commencement of sexual activity.
- Catch up vaccination is recommended in case of incomplete vaccination.
Preconception counseling /pregnancy planning

Preconceptional Counseling / Pregnancy planning
- FOGSI recommends vaccination counseling as apartof pre-pregnancy counseling .(unvaccinated women)
- History of occurrence of vaccine preventable diseases, previous vaccinations administered and allergic reactions to vaccinations must be recorded.
- Rubella ,Hepatitis B and Varicella vaccination should be given preferably during postmenstrual period
- Rubella ,Hepatitis B and Varicella vaccination should be given preferably during postmenstrual period
Rationale for rubella vaccination
Context :
- Immunization programs worldwide have made a major impact in the epidemiology of rubella both in the developed and several developing countries.
- In the US total cases decreased from 58 /100000 population in 1969 to 0.5 cases /100000 population in 1983 as a result of the effective MMR vaccination.
- In a study from Vellore it is reported that congenital rubella constituted about 9.8 % of all children born there with suspected congenital infections
- Hepatitis B vaccination with an ongoing pregnancy is safe and doesnot warrant a termination.
- HPV vaccination should be considered in this age group .In case the woman becomes pregnant after receiving the first dose of HPV vaccination, the next dose should be deferred; however there is no need to terminate the pregnancy.
- The rest of the dosages can be completed after delivery.
- Tetanus and diphtheria immunization can also be considered.
Vaccination during pregnancy
FOGSI recommends immunization against tetanus, diphteria,pertussis and influenza during pregnancy
Two doses of tetanus toxoid injection at least 28 days apart are to be given to all pregnant mothers commencing from second trimester.
If the subsequent pregnancy occurs within 5 years only one booster is given.
Context
- In contrast to developed nations where tetanus is rare ,it remains endemic in the developing world .
- The incidence often increases following natural disasters such as earthquakes and tsunamis .
- n 2012 there were 2404 cases of tetanus reported to the WHO from India4
- Tetanus diphtheria acellular pertussis (T-dap) vaccination can be considered instead of the second dose of tetanus toxoid to offer protection against diphtheria and pertussis in addition to tetanus.
- The regular pertussis vaccine is contraindicated in pregnancy.
- (Tdvac) tetanus and diptheria vaccination can be an alternative if T-dap is not available.
Context :
- In the year 1997 and 1998 the number of diphtheria cases reported to the WHO from India were 1326 and 1378 respectively. Since then there has been a steady rise in theincidence of the disease. This has now plateaued over the last 5 years.
- In 2012 a total of 2525 new cases of respiratory diphtheria were reported from India. For reasons that are not well understood pockets of diphtheria are reappearing primarily in developing countries
- IAP suggests immunization of pregnant women with single dose of Tdap during the third trimester (preferred 27 - 36 weeks gestation) regardless of the interval between previous Td or Tdapvaccination. Tdap has to be repeated in every pregnancy irrespective of the status of previous immunization

Flu season is here...
Protect two from the flu and get Vaccinated inday
vaccination is recommended for mothers from 26 weeks
Influenza vaccination is recommended for mothers from 26 weeks onwards
In case of a pandemic the influenza vaccine can be given earlier to protect the mother
Context:
- Both influenza A and B viruses are important as respiratory pathogens .
- nfluenza occurs all over the world with the annual global attack rate estimated at 5-10% in adults and 20-30% in children .
- Most of the infections globally are caused by influenza A(HINI),Influenza A( H3N2) and Influenza B viruses.
- Antigenic drift’ results in seasonal epidemics and is due to point mutations that occur during viral replication.

H1N1
Higher rates of influenza associated complications recorded among pregnant women during the 2009 H1N1 pandemic resulted in recognizing pregnancy as a high risk group and therefore vaccination is recommended in this group.
Studies have demonstrated a 63% reduction in influenza illness among infants up to 6 months whose mothers received influenza vaccination during pregnancy
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommend that all adults receive an annual influenza vaccine. Influenza vaccination is an essential element of preconception, prenatal, and postpartum care because pregnant women are at an increased risk of serious illness due to seasonal and pandemic influenza.
H1N1
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommend that all adults receive an annual influenza vaccine. Influenza vaccination is an essential element of preconception, prenatal, and postpartum care because pregnant women are at an increased risk of serious illness due to seasonal and pandemic influenza.
Influenze Vaccination During Pregnancy
Abstract :
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices and the American Collage of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recooended that all adults recive an annual influenza vaccine. Influenze vaccination is an essential element of preconception, prenatal, and postpartum care because pragmant women are at an increased risk of serious illness due to eseasonal and pandemic influenza
Postnatal vaccination
FOGSI recommends postnatal rubella ,hepatitis B, varicella,Influenza, tetanus and HPV vaccinations to all non immunized postnatal mothers .
Context :
- Postnatal period is a good window of opportunity which should not be missed to protect the mother and her future progeny.
- Influenza vaccination of the pregnant and parturient woman reduces the risk of respiratory illness including laboratoryconfirmed influenza in their infants up to 6 months of age as a result of both tranplacental maternal antibodies, and increased anti-influenza antibodies in breast milk
- Vaccines such as rubella can be safely administered in concurrence with postnatal contraception.

Cocooning:

Adolescents and adults (parents, siblings, grandparents, child-care providers, and health-care personnel) who have or anticipate having close contact with an infant aged <12 months should receive a single dose of Tdap to protect against pertussis if they have not previously received Tdap
Vaccination in adult and elderly women
Vaccination in adult and elderly women
- HPV , tetanus ,diphtheria and influenza for women of all ages
- Tetanus booster dose to be given once every 10 years throughout the life.No booster dose is necessary in case of an injury or a surgery within 5 years of vaccination. Td can also be given throughout life in place of tetanus toxoid
- Influenza vaccination annually can be offered to all women. The live attenuated vaccine is recommended up to 49 years of age and after that .
- HPV vaccine is licensed to be used up to 45 years of age
- Unvaccinated adults of age 65 years and older be vaccinated by Tdap
vaccination in women
Important points

- The clinician should be well informed about the correct dosages, storage recommendations, contraindications and adverse reactions of all vaccines.
- Whenever these infections are identified the appropriate authority in your locality should be informed.
notifiable diseases


Ignorance is always afraid of change.
Jawaharlal Nehru